NASA shares first look at 'city-destroying' asteroid set to hit Earth
- Research Validates That Asteroid Bennu Contains the Elemental Building Blocks of Life.
A city-destroying asteroid with the potential to head towards Earth is featured in a new video, offering a first glimpse of what is approaching.
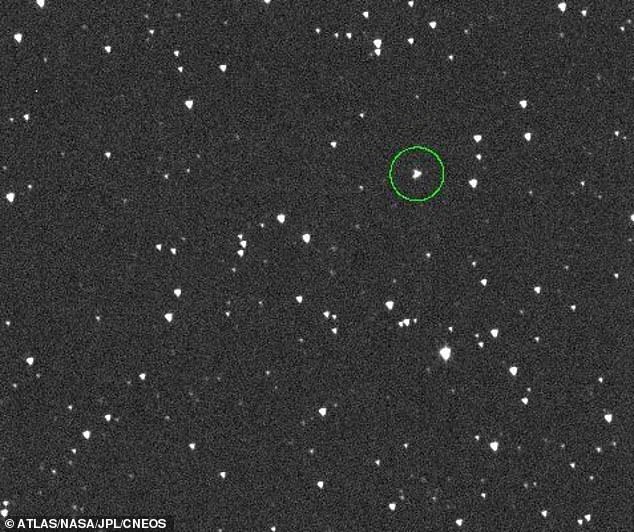
NASA spotted a roughly 200-foot-wide space rock, labeled asteroid 2024 YR4, approximately 35 million miles away from our planet.
The video depicted the asteroid as a bright, rapidly moving white dot soaring through the blackness of space, against the backdrop of numerous other glowing celestial objects.
.
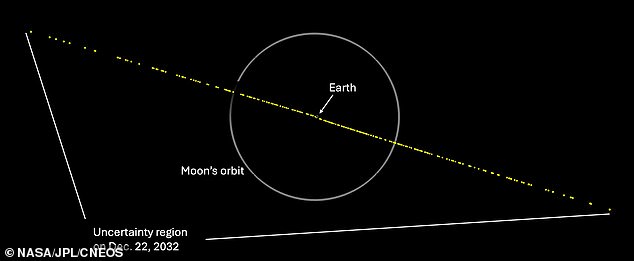
The initial detection enabled them to capture images of the celestial body's trajectory, showcasing it careening through space as it orbits the sun in an elliptical shape.
The Sentry system's automated list of potentially hazardous nearby objects, which ranks known Near Earth Objects (NEOs) based on their likelihood of colliding with our planet.
'As is common, the initial orbit was calculated with some degree of approximation, and the predicted uncertainties for 2032 were substantial enough to make the likelihood of the object being on a precise collision course extremely low,' the space agency stated.
As further observations are taken, the orbit has become more precisely defined, and the predicted possible range of positions for the Earth in 2032 has significantly narrowed down, with the Earth still falling within the swath of possible locations.

it will have a significant impact, especially if it lands in a densely populated area like a major city.
When it pierced the Earth's atmosphere in 1908, reportedly causing the deaths of three people.
The explosion detonated in the air over Siberia and caused an impact similar to detonating 50 million tons of TNT. As a result, an estimated 80 million trees across an area of 830 square miles of forest were flattened.
If object 2024 YR4 enters Earth's atmosphere, it could possibly disintegrate in mid-air like the Tunguska asteroid.
Asteroid 2024 YR4 is projected to potentially collide with Earth, landing somewhere along a hazard zone that spans across the eastern Pacific Ocean, northern South America, the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Arabian Sea, and South Asia, according to NASA.
But astronomers also state that it could possibly remain intact during its descent and slam into the ground, resulting in the formation of a massive crater and causing devastation to human communities within the impact zone.
Astronomers have identified the 'risk corridor' or the area where the asteroid '2024 YR4' is likely to impact, following preliminary observations.
In addition, the potential for 2024 YR4 to cause damage will be determined by a more precise calculation of its size as well as its internal characteristics and composition that scientists are still gathering information on.


As the asteroid draws nearer, astronomers should be able to conduct more detailed observations, which can help them comprehend the asteroid's exact size, composition, and structure, specifically that of 2024 YR4.
Regardless, the chances of 2024 YR4 impact are low. According to astronomers, it is much more probable that this asteroid will safely pass by our planet in 2032.
In fact, astronomer and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) professor Richard P Binzel said to Wander Thoughtsthat he believes the likelihood of a direct impact will eventually become virtually non-existent.
"We anticipate that the probability will fluctuate for a while until we collect more observations that allow us to more precisely determine the asteroid's orbital path," he said.
"This is simply how scientific data measurements unfold," he said.
Astronomers will closely monitor the space rock over the next eight years to better understand the potential risks it poses to Earth.
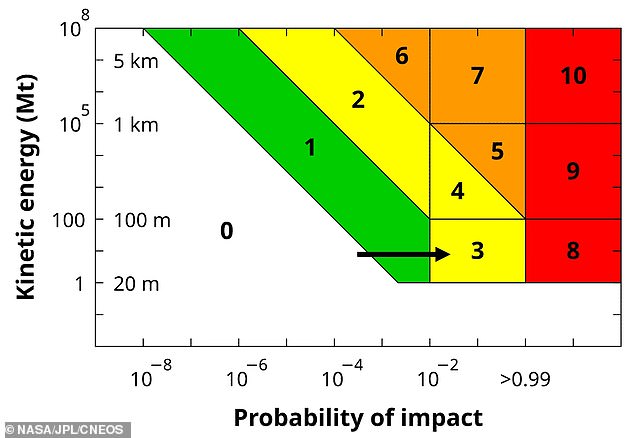
At present, asteroid 2024 YR4 is assessed as having a level 3 rating on the Torino scale, a methodology for classifying potential Earth impact hazards.
A rating of three implies the asteroid deserves attention from astronomers, as it is likely to have a close encounter with Earth and poses a larger than one percent chance of impact.
It's a scale from zero to 10, with higher numbers indicating a higher level of potential impact.
Most Near Earth Objects never reach a leveleven on the scale.
Now that 2024 Object 4 has been identified as a prospective – but improbable – peril, the pursuit to gain as much knowledge about it as possible before 2032 has begun.
Read more